
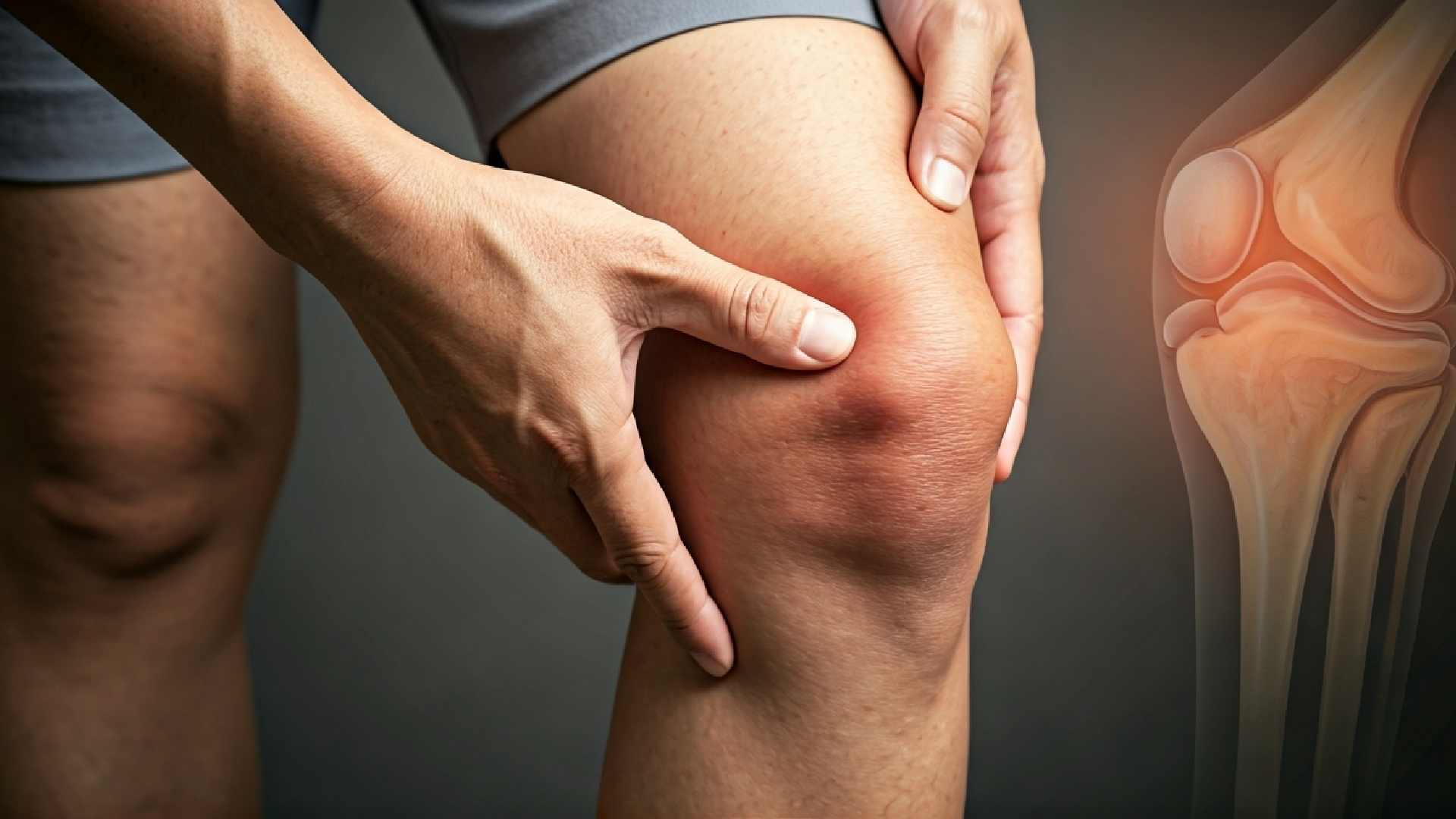
Osteoarthritis of the knee is the most common form of arthritis affecting the knee. It occurs due to wear and tear. This kind of arthritis affects the cartilage found in the knee joint.
The primary symptoms of osteoarthritis include persistent knee pain, stiffness in the knee, swelling, and limited knee mobility. It can also lower your range of motion.
Several risk factors increase your likelihood of developing knee osteoarthritis. These include age, genetics, excess body weight, and a history of recurring injuries.
Effective treatment plans for knee osteoarthritis typically involve modifying certain aspects of your daily life, engaging in physical therapy, taking the appropriate medications, and, in the most severe cases, undergoing surgery.
Maintaining a healthy body weight and engaging in gentle, low-impact exercises that are knee-friendly can help slow the progression of the disease. These steps can also provide relief from pain.
Physical therapy and joint replacement surgery are used to help restore movement and improve quality of life, enabling people with knee osteoarthritis to enjoy a better everyday experience.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a type of arthritis that worsens over time. It is one of the main reasons people get joint pain and have trouble moving. This problem starts when the cartilage in your knee wears down. As a result, the bones can rub against each other. This causes a lot of pain and makes it hard to move. Many people over the age of 50 experience this, but factors such as lifestyle choices and past injuries can also contribute to it. To stay on top of osteoarthritis of the knee, it is essential to understand its causes. You should also be aware of the symptoms and the available treatments. This can help you take control and get back to a better daily life.
Osteoarthritis of the knee, also known as wear-and-tear arthritis, is the most common type of arthritis that affects the knee joint. In this condition, the cartilage found between the bones wears down over time. This creates more friction between the bones in the knee joint, causing pain when you move.
This condition worsens over time, particularly in joints that support your weight. Many people in the U.S. have this condition, and it can make it difficult to walk, go up or down stairs, or perform regular daily tasks. That is why it is essential to identify osteoarthritis of the knee early and take appropriate steps to manage it. This helps keep your movement and comfort for as long as possible.
When osteoarthritis affects the knee, the primary issue is the breakdown of cartilage. This soft layer in the joint thins out with time. As a result, the bones start to rub against each other. This creates pain and reduces the knee’s ability to absorb shock during movement. The loss of cartilage also makes it hard for the knee to handle everyday activities.
Over time, the rubbing at the ends of the bones can lead to the formation of bone spurs. These are small, hard bumps that form where the cartilage has worn down. Bone spurs can cause the knee to become stiff and painful. They can also make it hard for you to move your leg.
The cartilage’s breakdown often leads to swelling and redness in the joint. As osteoarthritis gets worse, the knee may feel like it could give way or even lock up when you move it. These problems illustrate just how challenging living with knee osteoarthritis can be and why the right care and treatment for the cartilage and the ends of the bones are so crucial.
Several types of arthritis can affect the knee. Each type has its cause and a specific way it worsens over time. One common type is rheumatoid arthritis. This is an autoimmune disease. It happens when the immune system attacks the cartilage in the joints, including the knees. This leads to swelling and damage.
Inflammatory arthritis is another type. Some forms of this are psoriatic arthritis and reactive arthritis. In these cases, the immune system targets the tissues in the joints. This can cause pain and swelling.
Degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis, is the most common type of arthritis. Here, the cartilage in the knee wears down slowly over time. This is different from an autoimmune disease. This type of arthritis typically develops with age, following injuries, or due to excessive stress on the knee.
Understanding these types and their functions is crucial. It helps doctors and people with arthritis gain a better understanding of the type of arthritis they have. This makes it easier to plan the right way to check and treat it.
Knee osteoarthritis often develops due to the natural wear and tear of daily activities. However, there are other reasons as well. The risk increases as people age because the joints lose their natural padding. Certain risk factors exacerbate the issue. These risk factors include family history, carrying extra weight, old injuries, and performing repetitive tasks that involve heavy knee use.
The loss of cartilage in the knee is a natural part of the aging process. However, you can still take steps to help your knees. Try to identify and address some of the potential causes. This means shedding extra weight and avoiding undue stress on your knees by repeating the same tasks. If you work on these, you may lower your risk of developing knee osteoarthritis or slow its progression.
Age is important because, as people age, their cells become less effective at repairing cartilage. This makes damage to the knee joint easier to see. As you age, you have a higher chance of getting knee osteoarthritis. Genetics can also play a role. If someone in your family has cartilage problems or diseases like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, you could be at higher risk.
What you do every day also matters. Carrying extra body weight puts more pressure on your knees. Every pound added puts about four pounds of pressure on your knee joint. This breaks down the cartilage more rapidly over time.
Repeating the same movements over and over—such as kneeling, squatting, or lifting heavy objects—places additional stress on your knees. Making good lifestyle changes, such as regular low-impact exercise and a balanced diet, can also be beneficial. These steps can support your knee joint health and help slow down cartilage damage.
Secondary osteoarthritis differs from primary osteoarthritis. This type has clear causes. One cause can be autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In this, the immune system attacks the joint tissue. This leads to swelling and cartilage damage.
There are other related conditions, such as infectious arthritis or psoriatic arthritis, that can also trigger osteoarthritis. These can weaken the knee joint over time. Old injuries, such as fractures or past surgeries, can also increase the risk of complications. That is because the joint or cartilage may not heal as well as it was before.
Some less common illnesses, like hemophilia or Paget’s disease, may also harm the knee joint. These illnesses make it weaker. Addressing these issues early can mitigate their impact on the development of osteoarthritis. Early help can also lead to more effective ways to prevent further trouble.
When healthcare professionals use these tests, they obtain a clear picture of what is happening in your knee. This helps them give you the right treatment for your osteoarthritis.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis in the knee usually start mild. You may experience knee pain when you move or notice that your knee is stiff after resting. As time passes, these symptoms worsen. You may experience swelling, and your knee may not move as well as it did before. This can make it hard to do daily activities, such as walking or going upstairs.
If knee osteoarthritis gets worse, you could feel your knee lock. Sometimes it might even give out or make crackling sounds when you move. If you notice these early signs, it is important to see a doctor. Acting early can help prevent things from getting worse and maintain a better quality of life.
The early signs of osteoarthritis often begin with mild changes that many people overlook initially. Here are some warning symptoms to look out for:
These signs can come on slowly. Over time, they can continue to come back if you do not seek help. This will make it hard to enjoy normal movement or exercise. It is beneficial to act early and try to manage the discomfort, so it won’t prevent you from doing the things you want to do.
Over time, knee osteoarthritis typically worsens. At first, there may be only mild pain. But as the years go by, this pain can turn into chronic pain that will not go away. This pain can make it challenging to move around and lower your quality of life, especially in later years.
As knee osteoarthritis worsens, joint problems become more prevalent. The knee can feel loose or give out, and it might even lock during movement. Bone spurs can grow, and you may lose the ability to move your knee well. Simple things like going upstairs or walking can be tough.
As knee osteoarthritis progresses to later stages, it can become very challenging to perform daily tasks independently. You may not be able to remain as independent as you were before. If you understand how the condition progresses over time, you will have the opportunity to create a treatment plan early and help yourself while you still can.
Healthcare providers begin by examining symptoms and signs that indicate knee damage to determine if a person has knee osteoarthritis. They also ask about the person’s medical history. This helps them understand old injuries, family health issues, or factors that can put extra strain on the knee.
Doctors may check how well the knee can move and look for swelling. They also want to assess the stability of the knee. If they require additional information, they may use imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, to examine the inside of the knee and identify any potential damage.
These steps enable doctors to gain a deeper understanding of the condition. They can then create a personalized treatment plan that best suits each individual and their specific case of knee osteoarthritis.
A physical exam is crucial when your healthcare provider wants to determine if you have knee osteoarthritis. In this exam, the doctor looks at your knee. They check for swelling, assess your pain levels, and observe the overall appearance of your knee. The doctor may also observe you walking to evaluate whether your gait is affected. They will feel your knee joint to check if it is stable or loose.
Your medical records also help the doctor understand your condition. A patient’s medical history, including any previous injuries or diseases that may affect cartilage or compromise joint stability, is useful. Your family’s health history and any autoimmune issues can provide clues to what is happening.
To develop the best plan, your doctor will track the helpful pain relief, the treatments you have tried before, and which activities are currently strenuous for you. By putting what they learn from the physical exam together with your medical history, the doctor can give you the right help for knee osteoarthritis.
Some tests can help a doctor determine if you have knee damage associated with osteoarthritis. The main way is with imaging. X-rays can show if the cartilage is worn down or if you have bone spurs. MRI scans are used to get a closer look at soft tissues around your knee. Some cases may require a CT scan, especially if the condition is unclear or complicated.
Doctors also often run laboratory tests. These tests are necessary to ensure that you do not have other underlying conditions, such as autoimmune disorders. They examine joint fluid for any abnormalities and conduct blood tests to look for specific signs of other diseases. (Table…)
These types of tests help your doctor determine if you have osteoarthritis of the knee. The doctor can then pick the best way for you to get care at the right time.
There are several ways to achieve pain relief from knee osteoarthritis without undergoing surgery. You can start by making lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy weight helps alleviate stress on the knee joint. This will make it feel better. Physical therapy is good, too. It can improve your range of motion and also help strengthen the muscles around your knee.
Some people use dietary supplements to help maintain their joint health. Various medications can help alleviate pain and swelling, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Steroid injections are another choice. These give temporary pain relief. They allow you to do your activities of daily living with minimal pain. There are many things you can use together to get through each day with less discomfort.
Making simple lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis in the knee. Keeping a healthy weight is good for your body. It puts less stress on your knee joint and may help reduce joint pain and stiffness. You can try low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling. These types of moves help improve your flexibility and enhance your range of motion. Exercise can also make your body produce more joint fluid, which is helpful for knee health.
For quick pain relief at home, consider using a heat or cold pack on your knee. Some people also claim that dietary supplements, such as glucosamine and omega-3 fatty acids, can help alleviate swelling and maintain cartilage health. Try these changes and see if you experience better results in managing symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
For individuals with knee osteoarthritis, combining medication and physical therapy can be highly beneficial. NSAIDs give pain relief and help lower swelling in the knee joint. This can help alleviate joint pain and reduce stiffness. Physical therapy includes specialized exercises that help you move your knee more freely and strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint. Working with a physical therapist enables you to create a personalized treatment plan. This makes it easier to do daily things. It can also help you maintain a healthy weight and stay active.
Surgical treatments may be necessary when other methods for pain relief are ineffective or do not allow a person to use their knee joint as they did before. There are various types of knee surgery. Some are small and only clean the knee joint. Others, such as total knee replacement, are more complex and require a longer recovery time.
The choice of surgery depends on the person’s age, the severity of their arthritis, and their overall health. An orthopedic surgeon will review the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination, including an examination of the knee. The doctor will then use this information to pick the best option. The treatment plan should align with the person’s lifestyle and their specific needs for pain relief, such as after a knee replacement, to provide the most effective support.
There are several surgical options for treating knee osteoarthritis. These surgeries help improve the knee’s function and reduce pain. If you have a lot of knee pain because the cartilage is badly damaged, your doctor may suggest a total knee replacement. This surgery is common when knee osteoarthritis is severe. If your symptoms are not severe, a knee osteotomy may help. In this surgery, the knee joint is repositioned, allowing your weight to be spread out more evenly. Some people may need only a partial knee replacement. This replaces only the damaged part of the knee, so it’s less invasive than complete surgery. The right choice for you depends on your knee joint condition, the severity of your joint pain, your medical history, and your lifestyle. An orthopedic surgeon will discuss the best option with you.
After undergoing knee osteoarthritis surgery, it is essential to follow a clear recovery and rehabilitation plan. This plan helps you get back your knee’s movement and function. Initially, focus on improving your range of motion, which most people achieve with the assistance of a physical therapist. As you get stronger and steadier, you will do special exercises. These are beneficial for managing joint pain and improving knee joint mobility. Maintaining a healthy body weight is also crucial. The less weight on your knee joint, the less stress and pain you will feel. Be sure to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. This will help ensure a smooth recovery.
Living each day with knee osteoarthritis can be tough, but there are some new ways to help with joint pain and make life better. Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, is beneficial for the knee joint. These activities help improve the range of motion and strengthen the knee. It is also essential to keep a healthy weight. This helps alleviate stress on the cartilage and gives the knee joint a rest.
Adding dietary supplements to your routine and incorporating physical therapy can also help alleviate pain. These steps support the knee joint and help people feel less joint pain during daily life. With these choices, many can enjoy their favorite things with more ease and for a longer time.
Managing pain and performing daily activities with osteoarthritis of the knee can help improve quality of life. Focusing on lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, can help reduce stress on the joints. Adding gentle exercises from a physical therapist can help improve your range of motion and can also ease the stiffness that comes with knee OA.
Using assistive devices such as knee braces can support you in your daily activities. Adding dietary supplements may also give you some pain relief. These can help strengthen your immune system, which may aid in managing this chronic condition.
Living well with osteoarthritis of the knee means considering all options that can help. You have to manage both the pain and how you live each day. Using pain relief methods, undergoing physical therapy, and maintaining a healthy weight can help the knee move more smoothly. The joint will work better, and you will have less pain.
If you discuss your needs with your doctor, you can develop a plan tailored specifically to you. The plan should include the right medicine and needed help from therapists. This will help lower chronic pain and support your daily life, even when you have this most common form of arthritis.
Understanding more about this form of arthritis and learning how to cope are important. These steps help you lead a good day-to-day life and maintain a healthy knee joint over the years.
Knee osteoarthritis cannot be fully reversed. However, you can manage how it worsens. With lifestyle changes, medicines, and physical therapy, you can help manage your symptoms. These steps can also help your knee joint function more effectively. Getting help early is key for good results.
Individuals with knee osteoarthritis should avoid high-impact activities. This means running, jumping, or anything that puts a lot of pressure on the knee. Sitting or standing for a long time and repeating the same knee motions can also exacerbate the issue. It’s better to try low-impact workouts, such as swimming or cycling. These will help keep your knees moving without putting too much stress on them.
To slow the progression of knee osteoarthritis, incorporate regular low-impact exercises into your daily routine. Try to keep a healthy weight. Eat a balanced diet that has some anti-inflammatory foods. You can also try physical therapy. Braces or orthotics may also provide support. These changes in your life can make a big difference to how you feel with knee osteoarthritis.
Natural remedies for knee osteoarthritis can include taking supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin. Omega-3 fatty acids and turmeric can also help. Engaging in home exercises may be beneficial for your knees. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can help alleviate symptoms and improve joint function. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
Surgery for knee osteoarthritis may be needed when other ways to help do not stop the pain. If you find it hard to move or do your daily activities, it may be time to think about surgery. When the joint worsens, you may experience significant pain and struggle to enjoy life. At this point, a doctor may say surgery is the best option.
Pioneering Interventional Pain Management
Delhi | Faridabad | Gurugram | Ghaziabad | Noida | Lucknow | Jaipur | Mumbai
© 2025 Nivaan. All Rights. Reserved