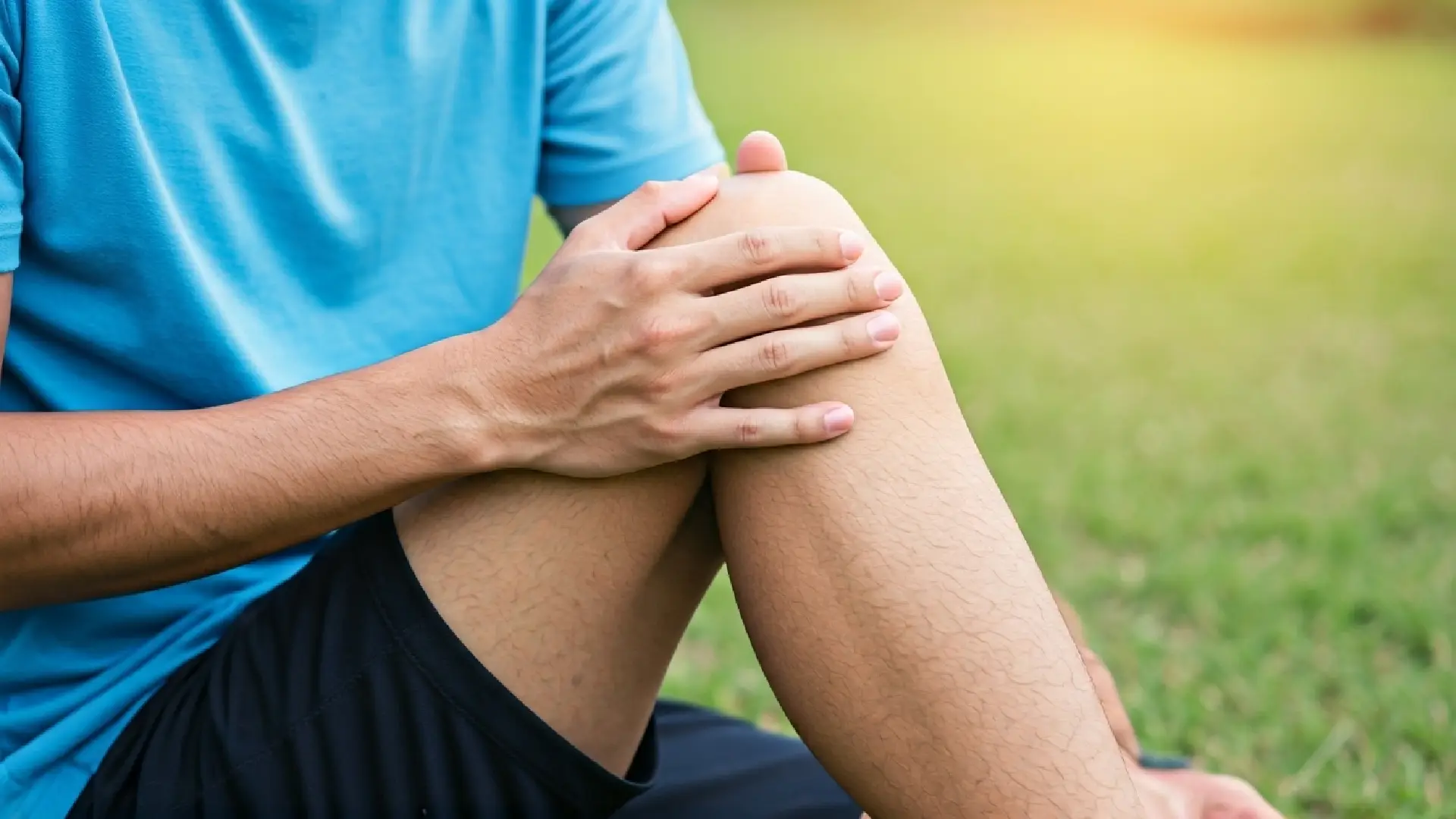


Sports injuries, overuse, or other medical problems often cause knee pain in young adults.
To understand why the knee hurts, it’s helpful to know how the knee joint works. You need to look at its bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
If you spot knee problems early, this can help stop long-term pain.
A good physical examination will help. Tests like MRI or X-rays will also help a doctor to know what is wrong with the knee.
Home remedies, a few lifestyle changes, and seeing a doctor when needed can help keep your knee healthy for a long time.
Knee pain is a common issue for young adults. It can interfere with your daily life and the things you enjoy doing. A sudden knee injury, overuse, or problems like adolescent anterior knee pain can cause this pain. Some knee aches resolve quickly, but others persist and require proper diagnosis and treatment. Young people can get knee problems from sports injuries or long-term issues such as arthritis. It is important to understand the causes of knee pain and the steps that can be taken to alleviate it. This helps you get back your movement and the good parts of your life.
The knee joint is the body’s most significant and most challenging joint. It helps hold heavy weight and lets you move. This joint is where the bones in the leg meet. Around those bones, the knee is composed of ligaments, cartilage, and tendons. These all work together to keep the knee stable and able to move. This structure allows you to bend, straighten, and even rotate your leg. Due to this, your knee joint is essential for activities such as walking, running, and squatting.
Understanding the functions of various parts, such as bones, ligaments, cartilage, and tendons, is a significant aid in determining the cause of knee pain. We will examine how every bone in the knee joint plays a crucial role in the knee’s functionality.
Your knee joint is made up of three important bones. These are the femur (or thighbone), tibia (also called the shinbone), and the patella (which is your kneecap). All of these bones meet and work together like a hinge. This is what lets you move the way you do every day.
The femur is the strongest bone in your body. It extends from your hip down to your knee and helps support you. The tibia fits with the femur. This bone holds up your knee and links it to your ankle. The patella, or kneecap, covers the joint to protect it. It protects the inside parts of your knee from too much rubbing as you move.
When these three bones meet and work together, you can walk, squat, or jump without trouble. However, if you have an injury, such as a fracture or a dislocation, you will likely experience pain. Your knee may become weak or wobbly. These bones form the main frame of the knee joint. The ligaments, tendons, and cartilage keep everything in the right spot so you stay steady as you move.
Ligaments, tendons, and cartilage all help keep the knee in its proper position. The knee has four main ligaments that act like strong ropes, providing stability and support to the knee. They stop the knee from moving out of place, either sideways or forward, and they hold the bones together. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the collateral ligaments are most known for helping keep the knee steady.
Tendons, such as the patellar tendon, connect the muscles to the bones. Cartilage acts as a cushion between the bones, providing padding. Articular cartilage lets the bones move smoothly against each other. The meniscus cartilage helps absorb shock and stress when people jump or run.
However, over time, these parts may become strained, torn, or worn down due to overuse or sports injuries. If this happens, the knee can be left vulnerable to further knee problems, such as arthritis and chronic pain. Now that you know the basics, let’s go over what can cause knee problems in young adults.

Knee pain is very common in today’s busy lives. It often happens because of sports injuries, trauma, or overuse. Young adults engage in a significant amount of physical activity. This can put a strain on the knee joint. Repeating the same motion over and over or using a poor technique can also harm the knee. Other factors, such as tight muscles, accidents, or conditions like arthritis, can also lead to a knee injury.
It is essential to determine the primary cause of knee pain. Taking prompt action—such as resting, undergoing a physical examination, or seeking medical help—can prevent more serious problems later. Now, let’s examine how sports injuries and repetitive activities can harm young knees.
Sports injuries are a leading cause of knee pain among young adults. Playing sports like soccer, basketball, and track can significantly injure the knee. You may see tears in the ACL or meniscus. After a sports injury, you may experience swelling, stiffness, or feel like your knee is unstable.
If the result of an injury is a very sore knee or significant swelling, you should take a break and consult a doctor. Sometimes, you need an X-ray or an MRI to know what is wrong with the injured knee. Initially, the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) can help reduce pain, lower swelling, and alleviate inflammation in the knee joint.
It is essential to warm up the body before playing any sport and to use the correct safety gear. This can help stop big sports injuries. Be cautious of overuse, as it can lead to long-term joint pain and knee issues.
Young adults often repeat the same physical actions. This can be biking, running, or squatting. When they repeat these activities, they may put too much stress on their knees. The tendons can become sore, and the muscles surrounding the knee can become tight. Over time, this can lead to chronic knee pain, such as patellar tendinitis, as overuse can damage the knee.
The signs can show up slowly. Some people start to feel stiffness or knee pain when they move in normal ways. Overuse injuries can affect various structures in the knee, including cartilage, ligaments, and the meniscus. If you ignore these problems, you can lose some of the knee’s range of motion. The knee may also feel weak for an extended period.
It helps to stop the activity that is causing pain in your knee. Performing simple stretches can also prevent the damage from worsening. Here, let’s look at some knee issues that affect young adults.
Certain conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome, inflammation, and Osgood-Schlatter disease mostly show up in young adults and teens. These issues often occur due to imbalances or weaknesses in the knee.
Getting ahead of these problems begins when you spot early signs, such as pain in the front of the knee, trouble bending, or swelling. To address these knee issues, consider incorporating exercise therapy, appropriate footwear, and effective training methods. Let’s begin by discussing patellofemoral pain syndrome, and then explore common knee issues affecting young adults.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome, or PFPS, is often called “runner’s knee.” It causes pain in the front of the knee. This pain occurs when the patella moves incorrectly or becomes irritated as it slides along the femur. Young athletes with PFPS may experience increased pain when climbing stairs, squatting, or sitting for extended periods.
This trouble can come from an imbalance between the quadriceps and hamstrings, tight muscles, or overuse. Treatment can include physical therapy. This helps to stretch tight muscles and build up strength, which can improve the way the knee works. Rest is important, too. Some people also need shoes that give good support.
It is essential to take action promptly if you have this problem, so the symptoms do not worsen. Another common problem for young people is Osgood-Schlatter disease, which typically appears during growth spurts and periods of increased activity.
Osgood-Schlatter disease affects young people. The main signs are pain and swelling under the kneecap, where the patellar tendon connects to the tibia. This often occurs when young people engage in a lot of physical activity while they are growing rapidly.
The usual symptoms are swelling and tenderness near the top of the tibia. Knee pain can worsen with increased physical activity. When you rest and engage in gentle exercise therapy, it often improves. Performing stretches for the quadriceps and hamstrings helps alleviate discomfort.
Instead of stopping all physical activity, people can engage in other types of exercise and wear protective gear to aid the healing process. If you notice symptoms of knee pain early, you can receive the right treatment more quickly.
Spotting symptoms of knee pain early can help keep your joints healthy. You may feel pain in joints, swelling, or stiffness. These signs often make it hard to bend your knee or climb stairs. The pain can be sharp, dull, or just aching. The way the pain feels may show what is causing it.
If you hear popping noises in your knee or have trouble straightening your leg, it could mean there is a problem with your ligament or meniscus. Understanding the relationship between knee pain, swelling, and feeling unsteady can help you make more informed choices about treatment.
Knee pain can manifest in various ways, such as anterior knee pain or a feeling of stiffness in the knee. This pain often occurs due to muscle strain or excessive physical activity. You may notice:
Treatments tailored to your knee pain can help you recover more effectively. Swelling and a feeling of instability in the knee can also help your doctor determine the cause.
Swelling in the knee can indicate strain from activity or an injury. Excessive use of your knee can lead to bursitis. This is when the fluid-filled sacs near the knee get inflamed. People with sports injuries often have swollen joints and feel instability.
If you have an injured knee, it may “give out” without notice. This often indicates ligament damage. If you continue to experience this instability, seek help immediately. Moving the knee without support can exacerbate pain or cause further damage. To determine the severity of a knee injury, a doctor must conduct a physical examination. This is important if you have swelling, overuse, or inflammation in the knee.
To determine the cause of your knee pain, a doctor will first conduct a physical examination. The doctor may also use imaging tests, such as an MRI or X-rays. If you experience swelling or are unable to move your knee, seek help immediately.
It is good to see a healthcare provider soon if your pain does not go away or gets worse. Getting care early can help fix the problem with your knee. If you wait too long, the pain could turn into a long-term issue. This could make you need surgery or many sessions of physiotherapy. Next, let’s discuss how doctors use specialized tests to diagnose injuries.
A thorough physical examination conducted by experts is crucial to determine the cause of the knee issue. Here is a simple look at the tools used to check for knee problems:
Tool
Application
X-ray
Indicates whether there are any broken bones or if the space between the joints is narrowing, as seen in osteoarthritis.
Magnetic Resonance (MRI)
Helps identify problems with soft tissues, such as ACL injuries or damage to the meniscus.
Ultrasound
It can help identify a cyst, bursitis, or any changes in the tendons.
Doctors will look at how the knee bends and straightens. They use stress tests to check for stability. This comprehensive and smooth method helps them create an effective treatment plan for knee problems.
Knowing how to spot urgent attention signals can help prevent knee injuries from worsening. Look out for these signs:
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek a referral to a doctor immediately. Getting help from a professional early can stop long-term joint issues. At home, treating pain begins by using simple measures to alleviate symptoms and keep your knee mobile.
Home remedies can help with knee pain. The RICE method stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. You can use this to reduce swelling and improve your overall well-being without the need for medication. Good shoes also help keep your body in better alignment and take strain off your knees.
You should change some activities. Try to avoid activities like squatting or heavy movements, as these can exacerbate knee pain. There are some over-the-counter medicines. NSAIDs like ibuprofen may give some relief for a short time if your pain is not too bad. Now, let’s look at some home-care steps, such as simple physical therapy at home and adjusting daily movements, to help support recovery.
Taking care of your knees at home is all about giving them enough rest. When you use an ice pack on your knee for 15 to 20 minutes every few hours, it helps reduce inflammation. Using wraps for compression can also help lower swelling.
Physical therapy exercises are beneficial for strengthening weak quadriceps and loosening tight hamstrings. This helps you bring back strength and movement in your knee. If you need pain relief, over-the-counter medicines like ibuprofen or naproxen can also help with inflammation. It is best to combine these treatments with rest to help your knee recover slowly.
Wearing supportive footwear is good for knee health. Engaging in physical activity reduces stress. Shoes with arch supports or orthotics help keep your knee and lower leg in the right place. Cutting down on exercises that put a lot of impact on your joints can help prevent overuse injuries and reduce pain.
When you use knee braces, they help keep the joint stable while you move around each day. If you are dealing with obesity, losing even a bit of weight can help with knee alignment and lower your pain a lot. Taking these steps will help you improve, especially if you also adjust how and when you perform your activities.
Understanding knee pain in young adults is crucial for maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. Many things can cause pain in the knee, including sports injuries, overuse, or other knee-related issues. It is crucial to recognize the signs of knee pain and know when to consult a doctor. This can help you recover more effectively and manage pain more effectively.
To prevent knee pain, use proper techniques when participating in sports or other activities. Wear shoes that support your feet, as this can help reduce the risk of injury. If you know more and take steps early, you can maintain your knee health. Young adults who do this may feel less pain and have a better time every year.
If you experience knee pain or are concerned about it, consult a doctor. It’s beneficial to receive advice tailored to your specific needs.
The leading causes of knee pain in young adults are sports injuries, repetitive strain from physical activity, and overuse. Problems such as ACL tears, patellofemoral syndrome, or arthritis can affect the knee joint. These conditions often affect the ligaments, tendons, or cartilage.
Yes, steady knee pain can be a sign of arthritis. It is most often seen with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. However, it is less common in young adults than in older people. Signs such as joint pain, stiffness, or swelling may indicate that you should consult a doctor. Only a doctor can tell if you have this type of arthritis.
To prevent knee pain during physical activity, start with a good warm-up. You can use knee braces and wear the right shoes. This helps you protect your knees. Stretching is also important because it can help loosen tight muscles. Do not push yourself too hard. Also, try to use moves that take stress off your knees when you work hard.
You should see a doctor for knee pain if you experience significant pain, swelling, difficulty moving your knee, or if it persists for more than a few days. Sometimes, you will need a referral if there is an injury, your knee looks different, or you have ongoing pain from some other problem.
Ignoring knee pain can lead to more severe knee problems in the future. Leaving it untreated can lead to chronic knee pain or even damage the knee joint for good. Over time, the pain may get worse. You may find it challenging to move around, or problems with alignment may become apparent. If things get worse, people can end up needing surgery for issues like arthritis or ligament tears.
Pioneering Interventional Pain Management
Delhi | Faridabad | Gurugram | Ghaziabad | Noida | Lucknow | Jaipur | Mumbai
© 2025 Nivaan. All Rights. Reserved