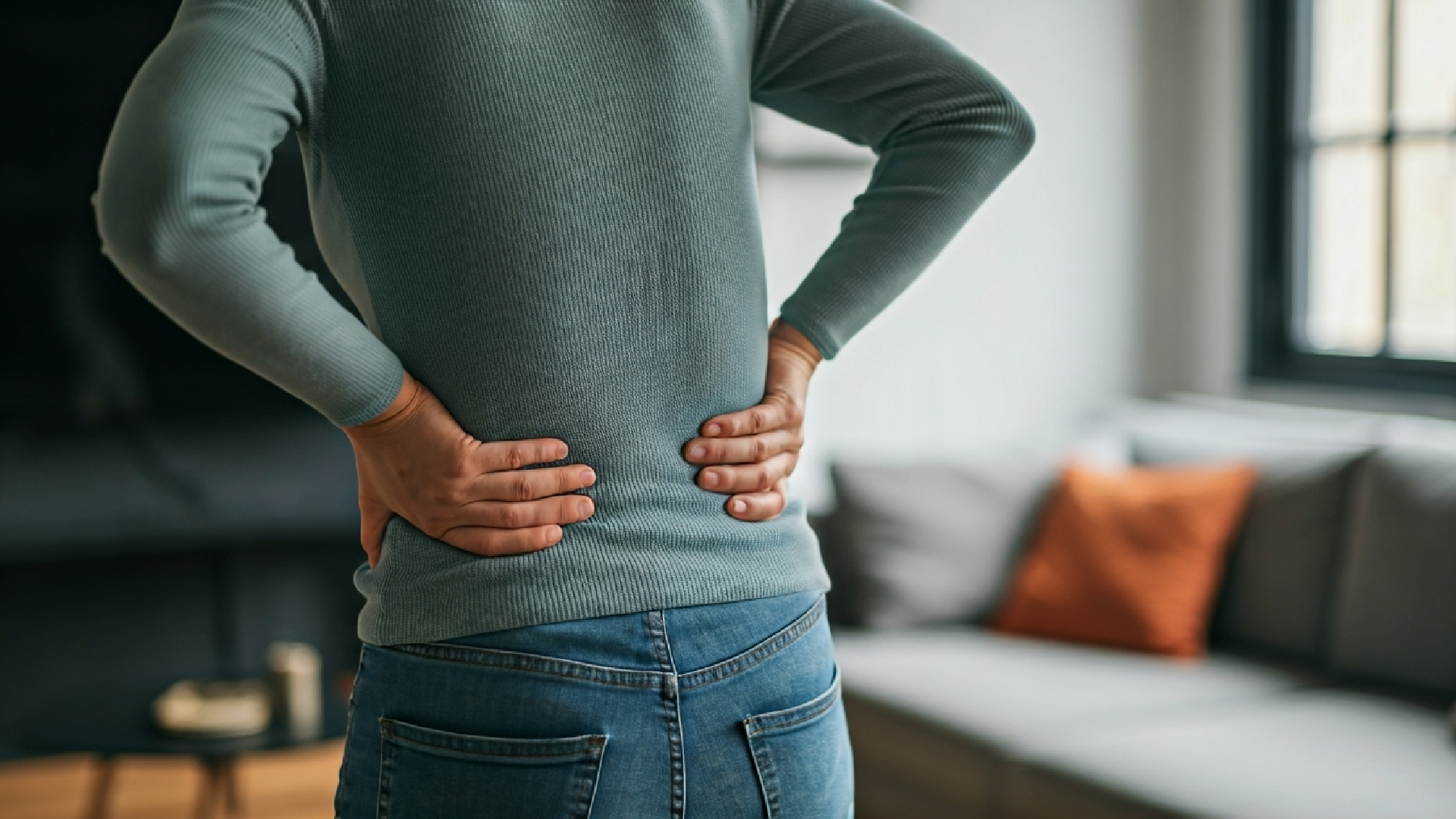


Middle back pain usually happens in the thoracic spine. This is the part between the shoulder blades and the bottom of the rib cage.
Symptoms of middle back pain can be sharp, dull, or aching feelings. These often come with stiffness and a limited range of motion.
Common causes of middle back pain include muscle strain, poor posture, herniated discs, and occasionally, kidney problems or other underlying health issues.
To determine the cause of the pain, doctors use a physical exam, review your medical history, and may order imaging tests.
Treatment options for middle back pain vary. They can include self-care, lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or medical assistance, depending on the cause.
Knowing the signs and risk factors early can help prevent middle back pain. It also helps in managing the pain and getting help on time.
Middle back pain is a common problem that can affect your daily activities. This pain comes from the thoracic spine, which is the part of your back from the base of your neck to the bottom of your rib cage. There are many possible causes of middle back pain. These include muscle strain, poor posture, and sometimes more serious problems like herniated disks or issues with your organs. Understanding what causes this pain is the first step to finding lasting relief.
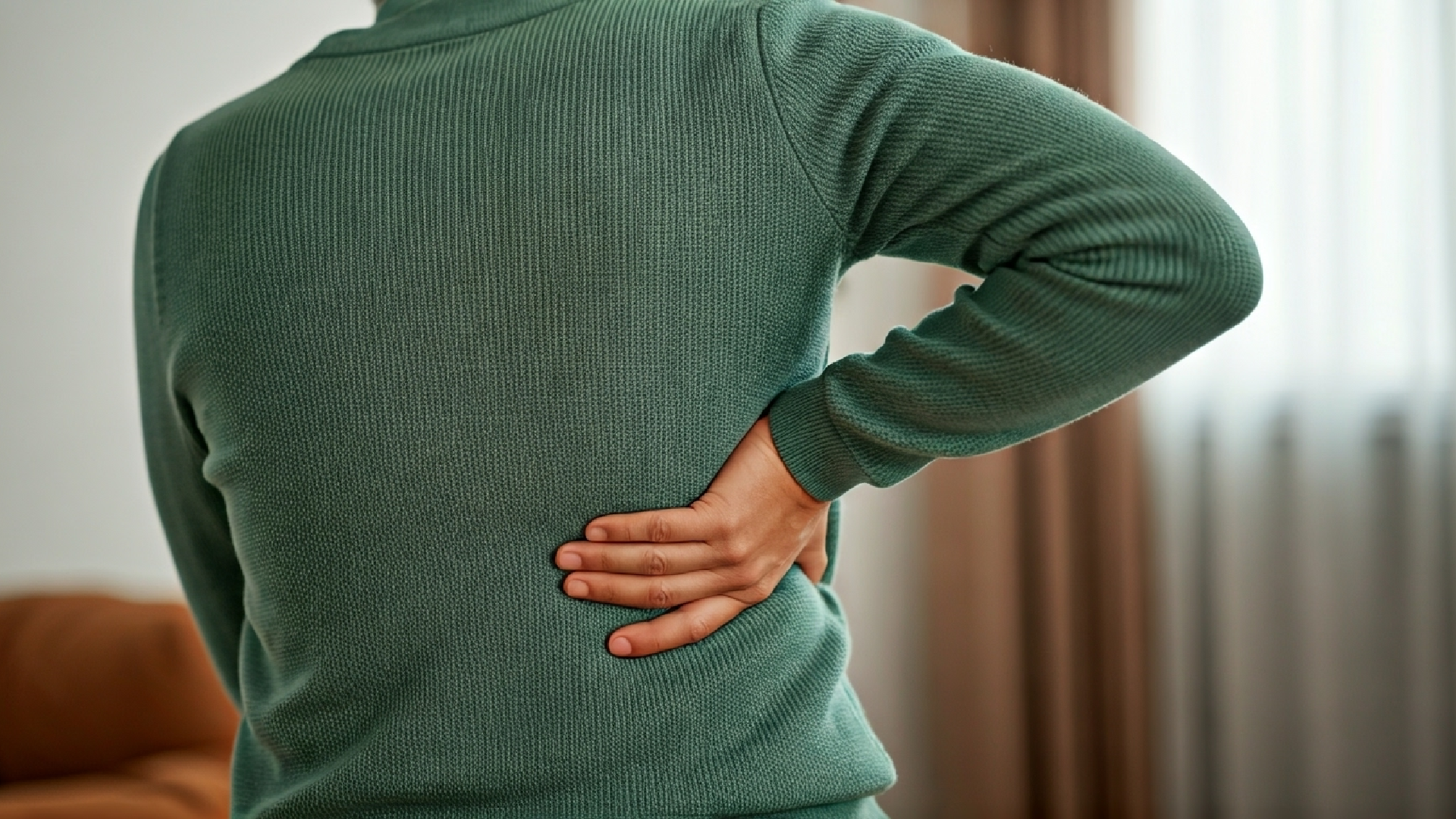
When you feel pain in your middle back, it is usually in the area called the thoracic spine. This part has many bones, disks, muscles, and ligaments. Because of this, it can hurt if it gets injured or stressed. Pain in this area can result from various mechanical or medical issues.
It is essential to recognize the various symptoms of middle back pain. These symptoms can range from a simple muscle strain to a more serious medical issue. If the pain is severe or persistent, identifying the underlying cause can help you receive the appropriate treatment and prevent it from recurring.
The middle back, called the thoracic spine, is the part between the base of the neck and the bottom of the rib cage. This area has 12 bones called vertebrae (T1 to T12). It is stiffer than the lower back. This helps provide support and protect vital organs, such as the heart and lungs.
The thoracic spine lies between the shoulder blades above and the rib cage below. It does not move as much as the neck or lower back. This limited movement helps protect the spine from harm in many cases.
Many muscles, ligaments, and nerves connect here. So, any wrong movement or tired muscles can cause pain and stiffness. Knowing the location of the thoracic spine helps you understand where pain originates and why.
Middle back pain is a significant health issue in India, affecting people of all ages, but most notably those between 30 and 50. The growing prevalence is tied to factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor workplace ergonomics, and rising obesity rates. Middle back pain now accounts for a substantial portion of disability and medical consultations.
Understanding the main risks — prolonged sitting, improper lifting, and weak muscle support — can help you take preventive measures. Workplace-related habits are especially influential in India’s urban workforce.
Here is a comparative text table summarizing the key aspects:
Factor
Details/Stats in India
Prevalence
Increases with age, common in ages 30-50
Risk of Back Pain
Heightened by sedentary jobs & obesity
Most Frequent Causes
Poor posture, muscle strain, and disk problems
Leading Cause of Disability
Medical Condition Links
Weight gain
Arthritis, osteoporosis, and kidney stones
Being aware of these facts empowers you to make healthier choices and seek care when necessary.
When you have middle back pain, it often feels like a dull ache or a sharp pain in the middle part of your back, called the thoracic area. You may experience this pain when resting, after engaging in an activity, or even immediately after waking up. This pain can make it difficult to move and cause you discomfort on a daily basis.
You might also notice that your back is sensitive to touch, the muscles feel tight, and your back feels stiff. Recognizing these early signs can help you begin to manage the pain and potentially alleviate it sooner.
Sharp, dull, and aching are the typical sensations people experience when they have middle back pain. Sharp pain may indicate that a nerve is irritated or damaged. Dull aches can show muscle strain or poor posture. Aching pain often comes from ongoing problems like degenerative disc disease. Knowing these types of pain helps doctors find the problem and create the right treatment plan. It is essential to understand your pain to receive proper care and effectively manage middle back pain.
Stiffness, trouble moving, and tingling often come with middle back pain. Stiffness can make it hard to move and cause pain. Trouble moving may make daily tasks hard. Tingling may indicate a problem with your nerves. This needs medical attention. It is essential to address these symptoms promptly. You can try physical therapy or make lifestyle changes. If you ignore these signs, the pain could get worse. This can hurt your quality of life. If you experience these symptoms of middle back pain, consult a doctor. They can help make a good treatment plan for you.
For many people, the main causes of middle back pain are linked to muscles and bones. Daily habits, such as muscle strain, prolonged sitting or standing with poor posture, and weak muscles that support the back, often contribute to the problem. Over time, these habits can cause changes in the structure of the back or irritate the nerves in the thoracic spine.
Sometimes, other health issues like herniated disks or diseases that wear down the spine can cause pain. Identifying these issues early helps to treat them more effectively. The leading causes of back pain in the middle back and the thoracic spine include:
Muscle strain or sprain in the middle back often causes pain and stiffness. This injury happens when the back muscles or ligaments get stretched or torn. It mostly occurs during heavy lifting, sudden twisting, or repeated movements. Sports injuries or strenuous activities performed with improper form also increase the chances of this problem.
Using improper lifting techniques puts more stress on the back muscles. This makes tiny tears more likely. Even simple daily actions, such as reaching, bending, or gardening, can cause strain if done without the right care or support.
Common signs are pain in one spot, swelling, and tenderness. The pain may worsen when you move, but it can improve with rest. To prevent these injuries from lasting a long time, it is essential to strengthen your back muscles and adopt proper lifting techniques.
Slouching at your desk or standing with rounded shoulders may feel fine at first. But poor posture is a main cause of middle back pain. Over time, these habits create muscle imbalance and put extra pressure on the thoracic spine. This raises your risk of pain and injury.
A sedentary lifestyle exacerbates the problem. When your back muscles don’t move or get stronger often, they lose tone. This means they can’t support your spine well. The mix of being inactive and having poor posture leads to both short-term and long-term pain.
You can reduce your risk of back pain by making simple lifestyle adjustments. Try to sit or stand up straight. Set up your workstation in a way that helps good posture. Take breaks to move around. Maintaining these habits can help reduce discomfort and keep your spine healthy over time.
A herniated disk in the thoracic spine happens when the soft tissue between two bones in the back breaks or pushes out. This problem is more likely to occur as people get older or from performing the same motion repeatedly. Sometimes, it can come from a sudden injury. If the disk presses on a nearby nerve, you may experience back pain along with tingling or weakness.
The pain from a herniated disk often gets worse with activities like bending, lifting, or twisting. The pain can also spread to other parts of the body if the nerves are squeezed. Some people feel a sharp, electric shock-like pain, especially if the spinal cord is affected.
If the injury is not treated, it can become a long-lasting issue, characterized by persistent pain and limited mobility. Receiving the correct diagnosis and treatment, such as physical therapy or, in some cases, surgery, can help alleviate pressure on the nerves and improve your mobility.
Osteoarthritis is a condition that typically worsens with age. Over time, the thin cartilage that protects the joints in the thoracic spine wears away. This causes the bones to rub against each other, which can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness. It is one of the most common types of arthritis that affects the middle back. It also leads to long-lasting back pain in many adults.
Degenerative disc disease also gets worse with age. It reduces the amount of movement in the spine and decreases the cushioning between the bones. At the same time, bone density decreases, making the vertebrae more susceptible to fracture. This is another reason why back pain in the middle back may occur more frequently as you age.
Engaging in exercises that benefit your joints, maintaining a healthy diet, and addressing even minor symptoms promptly can help keep your spine functioning optimally. These steps can also help alleviate pain caused by changes in the spine associated with aging.
Most middle back pain comes from strain or poor posture. But some causes are less common and more serious. Severe pain in the middle back can be a sign of a more serious health issue. This could be spinal fractures, infections, tumors, or kidney stones. These need a doctor’s check right away.
It’s important to know the “red flag” signs. These include unexplained weight loss, loss of bowel control, fever, or pain after an injury. If you have any of these, see a healthcare provider quickly. Your safety depends on it.
Traumatic injuries to the thoracic spine, like fractures, usually happen because of serious events. These include falls, car accidents, or direct hits during sports. Such injuries cause sudden and severe pain. The pain often worsens when you move or press on the affected area.
Fractures can also harm the spinal cord. This can cause severe symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, or loss of bowel or bladder control. You may need stabilization, imaging tests, and sometimes surgery. These help restore the spinal function and stop long-term problems. Receiving prompt treatment gives you the best chance to fully recover and avoid long-term harm.
Although it is rare, infections or tumors can occur in the thoracic part of the spine and require prompt attention. Infections may happen when bacteria enter the vertebrae or nearby tissues. This can cause persistent pain, swelling, fever, and even nerve problems.
Tumors can originate in the spine or spread to it from other parts of the body. People with spinal tumors often feel pain that gets worse slowly, especially at night. They may also lose weight without a clear reason or, in serious cases, feel weak or become paralyzed.
If you experience persistent pain that does not improve with usual treatment, fever, or any unusual changes in your health, consult a doctor. A comprehensive check-up can help you receive prompt and life-saving care for these serious health issues.
Kidney problems, such as infections or kidney stones, can cause pain in the mid-back area. This pain typically feels deep and sore, often near the lower ribs or on the sides. Often, pain from the kidneys can spread into the back, making it difficult to distinguish from normal muscle pain.
In these cases, other symptoms provide a clue: pain or burning when urinating, frequent urination, fever, chills, feeling unwell, or changes in your urine indicate that it is a kidney problem, not just a muscle strain. This pain persists and remains unchanged when you move or change position, which is distinct from most pain in the thoracic spine.
It is essential to identify the cause early, as untreated kidney problems can become severe and lead to complications. Always see a doctor if you think your back pain might be from an infection or kidney stones.
Certain factors can increase your likelihood of experiencing middle back pain. Being overweight, not moving enough, and work habits that put stress on your back raise the chances. Common causes include obesity, excessive sitting, and working long hours in environments that are not conducive to good health.
Fixing these risk factors early can help protect your spine. This means adopting better posture, exercising regularly, and being mindful of your work habits. These steps can keep your back healthy for a long time. Let’s look at how your lifestyle and daily habits affect how likely you are to get pain in your back.
Extra body weight puts constant pressure on your spine and the muscles that support it. Studies show that having extra weight raises the chance of having back pain, especially in the middle back area.
Not moving enough also weakens the muscles that keep your back steady. This makes it harder for your back to handle everyday activities. Over time, inactivity can turn small aches into long-lasting back pain.
However, small lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. Adding low-impact exercises, losing extra weight slowly, and building muscle strength can make a big difference. Even small steps in being more active and managing your weight can lower the risk of ongoing, serious back pain.
Your daily activities and work routines can quietly cause middle back pain if you do not handle them well. Jobs that involve sitting at a desk or tasks that require bending, twisting, or holding awkward positions frequently can cause pain and strain in the thoracic spine.
Using the wrong way to lift things—whether at work, home, or the gym—puts too much pressure on your back muscles and disks. Even chores at home or taking care of children can hurt your back if you don’t pay attention to how you move.
To protect your back, try to use safer habits. For example, lift with your legs instead of your back. Adjust your workspace to be more comfortable. Change your position often. Being aware of and maintaining good work habits can help prevent the causes of middle back pain.
To determine the cause of middle back pain, a thorough medical examination is necessary. The first step is to examine your symptoms, the activities you engage in, and whether you have had any recent injuries that might have caused the pain. Doctors will do a physical exam to look for tender spots, limited movement, or nerve issues.
If the pain is severe, persistent, or unrelieved, additional tests such as imaging may be performed. This helps identify any serious problems in the back. Knowing the warning signs early helps ensure the right treatment and a faster recovery.
When you see a healthcare provider for middle back pain, they will start by asking about your medical history. They want to know if you have had past injuries, ongoing health problems, or activities that might cause your pain. You should explain when and how your pain began. For example, did it start suddenly after lifting something, or did it develop gradually over time? This helps them understand your pain better.
Next, they will do a physical exam. They will assess your spine alignment, range of motion, muscle strength, and look for any signs that nerves are affected. The doctor might also look for areas that hurt, swelling, or unusual body postures.
This detailed check-up enables the healthcare provider to create the most effective treatment plan for you. If your pain is simple and does not come with serious signs, they might suggest home care and no extra tests.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRIs, become very important when your symptoms indicate a serious problem. This includes pain that persists, changes in nerve function, injury, or no improvement after the initial treatment. X-rays show the bones clearly. They can find fractures, wear and tear, or arthritis.
If there is a chance of herniated disks, nerve pressure, or tumors, an MRI is used. It shows detailed pictures of soft tissues, disks, and the spinal cord. These pictures help find the exact cause of pain. They also help doctors plan surgery or other treatments.
Although imaging is very helpful for specific problems, doctors typically recommend it only when necessary. This avoids conducting unnecessary tests. Talking clearly about your symptoms helps make these tests more accurate and useful.
Managing middle back pain typically occurs in stages. Many people find relief with home remedies. These include using heat or cold packs, changing activities, and doing gentle exercise or physical therapy. Starting these early can help reduce pain and help you recover faster without needing medication or surgery.
But if the pain stays or gets worse, other treatment options may be needed. These can include prescription medicines, special therapies, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause. Having a plan made just for you can give you the best chance to feel better for a long time.
Small changes at home can make a significant difference in managing middle back pain. These steps let you take control of your health:
By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can not only alleviate middle back pain but also prevent it from recurring. This will help you move more effectively and enhance your overall quality of life.
Physical therapy plays a key role in managing long-lasting or difficult middle back pain. A physical therapist creates a plan just for you. This plan helps build strength in weak areas and restores normal function.
Going to therapy regularly can help you heal faster and lower your chances of getting hurt again. Always consult a professional before starting new exercises, especially if you have other health issues.
When self-care does not work, over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and swelling. If the pain persists or lasts a long time, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants, more potent pain medications, or recommend steroid injections to manage persistent inflammation.
In rare cases, treatments like nerve blocks or small surgeries might be needed for herniated disks or spinal cord pressure. These are only used for patients who do not respond to other treatments or who experience worsening nerve problems.
A plan tailored just for you, with the right medicine or treatment, can not only ease pain but also help you return to your usual activities faster and improve your overall health.
To avoid middle back pain, it’s essential to develop good habits and adjust your daily routines. Keep good posture. Do regular exercise. Also, manage your weight well. These are the main ways to prevent pain. Making your work area ergonomic and working on your core strength will also help you stay strong and avoid pain.
If you incorporate these habits into your daily life, you can lower your risk of back pain. This will keep your spine healthy. It will also help you have a better quality of life.
Making changes to your work and home setup can reduce extra stress on your middle back. Try these easy tips:
These simple habits help protect your middle back and keep pain away over time.
Maintaining strong and flexible back muscles is one of the most effective ways to alleviate middle back pain. Regular exercise helps support your spine and also boosts your overall energy, balance, and mood.
Engaging in some form of physical activity every day—such as walking, swimming, yoga, or strength training—helps improve blood flow to your spine and maintain joint health. As you become stronger and more flexible, you reduce the risk of injury and chronic pain.
You don’t need big lifestyle changes; even small increases in daily physical activity can help alleviate back pain. The important thing is to keep it up. Staying active helps you stay strong and improve your quality of life.
It is essential to know when your symptoms require medical attention. If your middle back pain is severe, lasts more than a few weeks without improvement, or is accompanied by warning signs such as numbness, unexplained weight loss, or issues with your bowels or bladder, you should consult a doctor immediately.
In India, consulting a healthcare provider early can help identify the problem more quickly, prevent it from worsening, and facilitate a faster recovery. Trust your instincts if something doesn’t feel right. Getting help early is always safer.
Some warning signs indicate that you should consult a doctor immediately. These signs can show serious problems that need quick care:
Do not ignore these warning signs. Visiting a doctor promptly can protect your health and prevent long-term harm.
Choosing the right specialist is crucial for effectively managing middle back pain. This is not just for identifying issues, but also for determining the best rehabilitation, pain management, or care. This helps you get the best result for back pain in the middle back.
In short, understanding middle back pain is crucial in helping you manage and alleviate pain in that area. When you understand the symptoms and potential causes, you can take steps to improve your well-being. This may include using home remedies, making lifestyle adjustments, or consulting a healthcare professional. With the right information and help, you can manage the factors that cause your middle back pain. This will help you live a healthier and more active life. If your pain persists for an extended period or if you are concerned about your symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
Middle back pain can result from muscle strain, poor posture, or issues in the thoracic spine. It can also be caused by herniated disks, arthritis, or kidney stones. If the symptoms of middle back pain persist for an extended period or worsen, consult a healthcare provider to assess the condition.
Yes, stress and worry can cause muscles in the middle back to tighten. This can lead to aches or even long-lasting pain. When you experience emotional stress, your muscles often become tight, causing pain. To effectively manage this type of back pain, it is crucial to identify the underlying cause. Using relaxation techniques and making lifestyle changes can help alleviate pain.
Sleeping on your back with a pillow under your knees or lying on your side with a pillow between your knees helps keep good posture. This can stop pain in your middle back. Try to avoid sleeping on your stomach, as this can put pressure on your spine. Using a supportive mattress can also help reduce back pain.
Kidney problems can cause deep and severe pain in the middle back. This pain does not get better when you move. You may also experience other symptoms, such as fever, chills, or pain when urinating. If you see these signs, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. This helps identify the correct cause and receive the appropriate treatment.
Physical therapy and exercises such as upper back stretches, gentle yoga, and core strengthening are often recommended for middle back pain. A physical therapist can create stretches and workout plans just for you. This helps with healing and provides effective treatment options for the long term.
Pioneering Interventional Pain Management
Delhi | Faridabad | Gurugram | Ghaziabad | Noida | Lucknow | Jaipur | Mumbai
© 2025 Nivaan. All Rights. Reserved